This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Asteroid Ryugu's anhydrous ingredients come from afar, study suggests
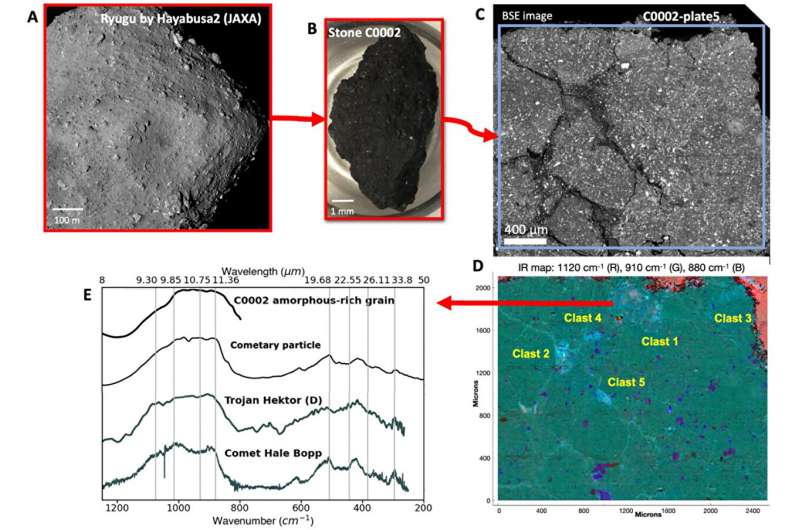
Infrared spectra of anhydrous grains from the carbonaceous asteroid Ryugu indicate a connection between one of the reservoirs from which Ryugu's parent body originated and the reservoirs that formed comets and primitive asteroids in the outer protoplanetary disk.
Ryugu is a second-generation carbonaceous asteroid formed by the reassembly of fragments from a previous larger body in the main asteroid belt. In late 2020, the Japanese mission Hayabusa2 returned to Earth 5.4 g of materials collected on Ryugu. The majority of samples consists of hydrated minerals which formed in Ryugu's parent asteroid by the aqueous alteration of primordial anhydrous grains. These grains reveal the composition of the protoplanetary dust from which Ryuguʼs parent asteroid formed.
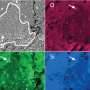
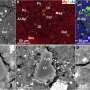
A new study led by IAS (Orsay, France), Tohoku University (Japan), and the SMIS beamline of synchrotron SOLEIL (France) used infrared hyperspectral imaging of two millimeter-sized "stones" of Ryugu to retrieve their mineral composition and to compare Ryugu with other extraterrestrial materials in the lab (meteorites and interplanetary dust) and in space (asteroids and comets). The study is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The infrared analysis of Ryugu's anhydrous grains shows that some of them are rich in amorphous silicates, with a mineral composition similar to that of some anhydrous primitive asteroids, comets, and interplanetary dust particles of cometary origin. These amorphous-rich grains formed by pre-accretional processes in the protoplanetary disk from which the solar system originated.
Ryugu's parent asteroid would thus be a large planetesimal that formed in the outer solar system from a reservoir close to the accretion region of comets. Planetary migrations would later have transferred Ryugu's parent asteroid to the main asteroid belt. Aqueous alteration would then have determined the spectral diversity of "primitive" asteroid classes we observe today.
More information: R. Brunetto et al, Ryugu's Anhydrous Ingredients and Their Spectral Link to Primitive Dust from the Outer Solar System, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2023). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/acdf5c
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal Letters
Provided by IAS Orsay