This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
ALMA spots the shadow of a molecular outflow from a quasar when the universe was less than 1 billion years old

Theoretical predictions have been confirmed with the discovery of an outflow of molecular gas from a quasar when the universe was less than a billion years old.
A quasar is a compact region powered by a supermassive black hole located in the center of a massive galaxy. They are extremely luminous, with a point-like appearance similar to stars, and are extremely distant from Earth. Owing to their distance and brightness, they provide a peek into conditions of the early universe, when it was less than 1 billion years old.
A team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Dragan Salak at Hokkaido University, Assistant Professor Takuya Hashimoto at the University of Tsukuba, and Professor Akio Inoue at Waseda University, has discovered the first evidence of suppression of star formation driven by an outflow of molecular gas in a quasar-host galaxy in the early universe. Their findings, based on observations they made using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), in Chile, were published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Molecular gas is vital to the formation of stars. As the primary fuel of star formation, the ubiquity and high concentrations of molecular gas within a galaxy would lead to a vast number of stars being formed. By ejecting this gas into intergalactic space faster than it could be consumed by star formation, molecular outflows effectively suppress the formation of stars in galaxies that host quasars.

"Theoretical work suggests that molecular gas outflows play an important role in the formation and evolution of galaxies from an early age, because they can regulate star formation," Salak explains. "Quasars are especially energetic sources, so we expected that they may be able to generate powerful outflows."
The quasar the researchers observed, J2054-0005, has a very high redshift—it and the Earth are apparently moving away from each other very fast.
"J2054-0005 is one of the brightest quasars in the distant universe, so we decided to target this object as an excellent candidate to study powerful outflows," Hashimoto says.
The researchers used ALMA to observe the outflow of molecular gas from the quasar. As the only telescope in the world that has the sensitivity and frequency coverage to detect molecular gas outflows in the early universe, ALMA was key to this study.
Speaking about the method used in the study, Salak said "The outflowing molecular (OH) gas was discovered in absorption. This means we did not observe microwave radiation coming directly from the OH molecules; instead, we observed the radiation coming from the bright quasar—and absorption means that OH molecules happened to absorb a part of the radiation from the quasar. So, it was like revealing the presence of a gas by seeing the 'shadow' it cast in front of the light source."
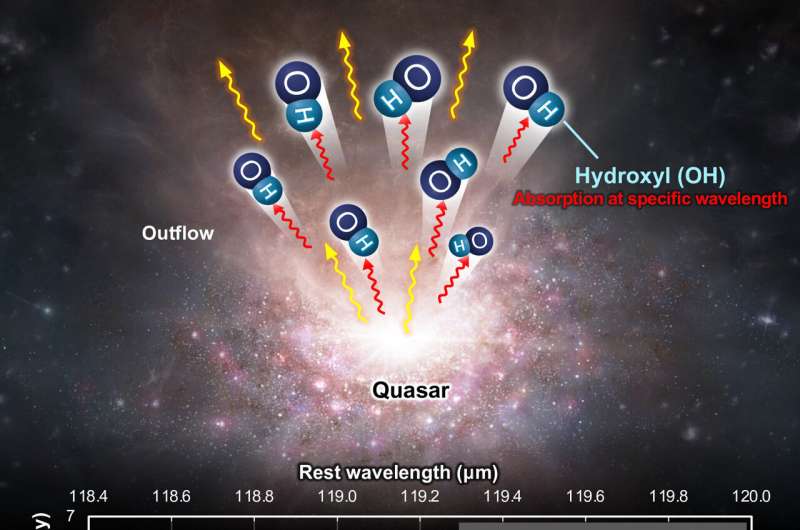
The findings from this study are the first strong evidence that powerful molecular gas outflows from quasar-host galaxies exist and impact galaxy evolution at the early cosmic age.
"Molecular gas is a very important constituent of galaxies because it is the fuel for star formation," Salak concludes. "Our findings show that quasars are capable of suppressing star formation in their host galaxies by ejecting molecular gas into intergalactic space."
More information: Molecular outflow in the reionization-epoch quasar J2054-0005 revealed by OH 119 μm observations, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0df5
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal
Provided by Hokkaido University