This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
AI-powered jet origin identification technology opens new horizons in high-energy physics research
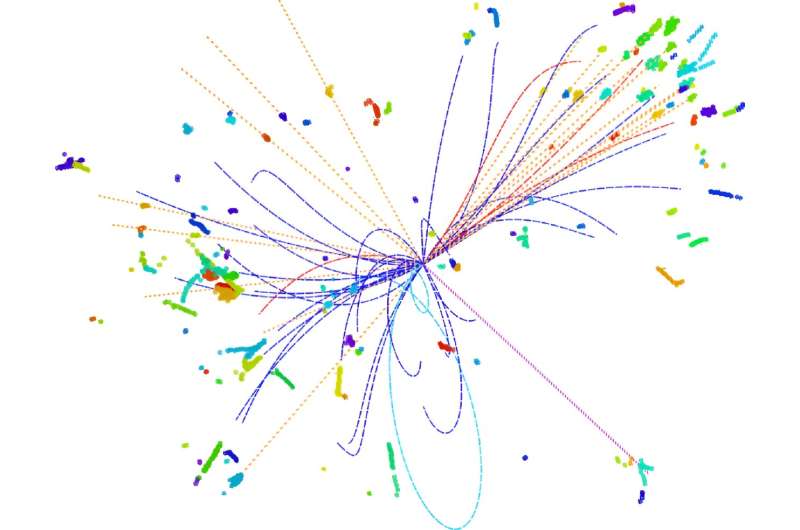
A research team in China has initiated and successfully developed a jet origin identification technology which can significantly enhance the scientific discovery capabilities of high-energy collider experiments.
The study, led by Prof. Ruan Manqi from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the team led by Prof. Zhou Chen from Peking University and Dr. Qu Huilin from European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), was published in Physical Review Letters on May 31.
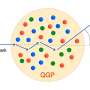
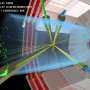
Quarks and gluons are fundamental particles in the Standard Model of particle physics. Unlike electrons or photons, they cannot move freely in space-time but are confined within composite particles such as protons or neutrons. Colliders can produce high-energy quarks, and their interactions lead to complex particle fragmentation processes, ejecting a large number of final state particles at specific angles. This phenomenon is known as "jets."
Jets are abundantly produced in high-energy collision experiments, and accurately identifying the origin of jets—i.e., determining which type of quark or gluon they originate from—is crucial for uncovering and understanding the physical laws behind collider events. On the other hand, jets originating from different quarks and gluons are very similar in configuration, making accurate identification of jet origins highly challenging.
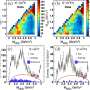
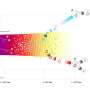
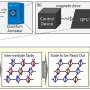
By combining the original high-performance particle flow reconstruction algorithm Arbor with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) technology ParticleNet, the research team developed an efficient jet origin identification technology.
This technology captures subtle differences between different types of jets, enabling efficient discrimination among eleven different types of jets produced by five types of quarks, five types of antiquarks, and gluons. It can help researchers accurately measure the interactions between different particles and quarks and gluons, and capture extremely weak Higgs particle decay signals. Also, it can significantly improve the precision of several key physical measurements in future colliders, greatly enhancing their scientific discovery capabilities.
This work not only provides researchers with a powerful new tool for scientific exploration in future colliders but also demonstrates that the complex information contained in the jet production process can be understood and utilized by advanced AI algorithms. In the future, the research team will explore the application of AI technology to broader and deeper high-energy physics problems.
More information: Hao Liang et al, Jet-Origin Identification and Its Application at an Electron-Positron Higgs Factory, Physical Review Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.221802
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences