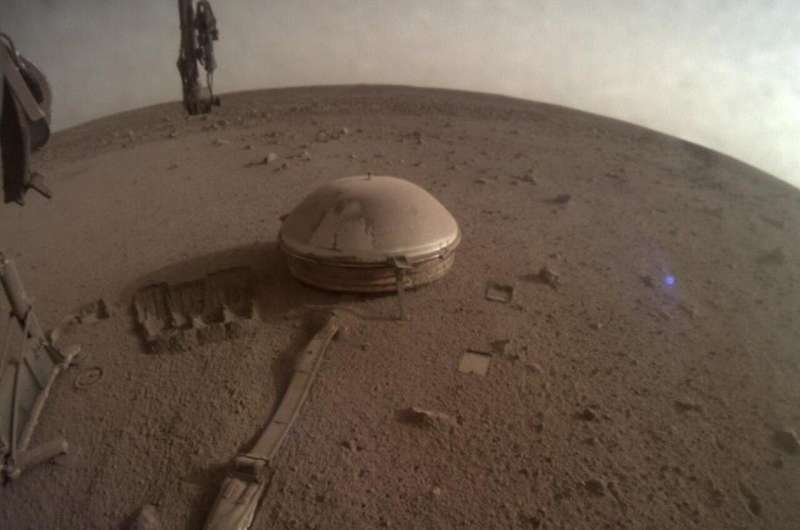
One of the last images ever taken by NASA's InSight Mars lander shows its seismometer on the red planet's surface in 2022. A team of scientists suggest that using data from the seismometer and a magnetometer on the lander could help reveal whether liquid water is present deep under the Martian surface. Credit: NASA
If liquid water exists today on Mars, it may be too deep underground to detect with traditional methods used on Earth. But listening to earthquakes that occur on Mars—or marsquakes—could offer a new tool in the search, according to a team led by Penn State scientists.
When quakes rumble and move through aquifers deep underground, they produce electromagnetic signals. The researchers reported in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets how those signals, if also produced on Mars, could identify water miles under the surface.
The study may lay the groundwork for future analyses of data from Mars missions, according to Nolan Roth, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Geosciences at Penn State and lead author.
"The scientific community has theories that Mars used to have oceans and that, over the course of its history, all that water went away," Nolan said. "But there is evidence that some water is trapped somewhere in the subsurface. We just haven't been able to find it. The idea is, if we can find these electromagnetic signals, then we find water on Mars."
If scientists want to find water on Earth, they can use tools like ground-penetrating radar to map the subsurface. But this technology is not effective miles under the surface, depths where water may be on Mars, the scientists said.
Instead, the researchers recommend a novel application of the seismoelectric method, a newer technique developed to non-invasively characterize Earth's subsurface. When seismic waves from an earthquake move through an aquifer underground, differences in how rocks and water move produce electromagnetic fields.
These signals, which can be heard by sensors on the surface, can reveal information about aquifer depth, volume, location and chemical compositions, according to the researchers.
"If we listen to the marsquakes that are moving through the subsurface, if they pass through water, they'll create these wonderful, unique signals of electromagnetic fields," Roth said. "These signals would be diagnostic of current, modern-day water on Mars."
On water-rich Earth, using this method to identify active aquifers is challenging because water exists in the subsurface even outside of aquifers, creating other electric signals as seismic waves move through the ground. This background noise must be separated from the aquifers' signals, the scientists said, for accurate identification and characterization.
"On Mars, where the near-surface is certainly desiccated, no such separation is needed," said Tieyuan Zhu, associate professor of geosciences at Penn State and Roth's adviser and co-author.
"In contrast to how seismoelectric signals often appear on Earth, Mars' surface naturally removes the noise and exposes useful data that allows us to characterize several aquifer properties."
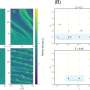
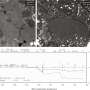
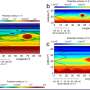
The researchers created a model of the Martian subsurface and added aquifers to simulate how the seismoelectric method would perform. They found they could successfully use the technique to analyze details about the aquifers, including how thick or thin they are and their physical and chemical properties, like salinity.
More information: N. Roth et al, Characterizing Liquid Water in Deep Martian Aquifers: A Seismo‐Electric Approach, Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets (2024). DOI: 10.1029/2024JE008292
Journal information: Journal of Geophysical Research
Provided by Pennsylvania State University