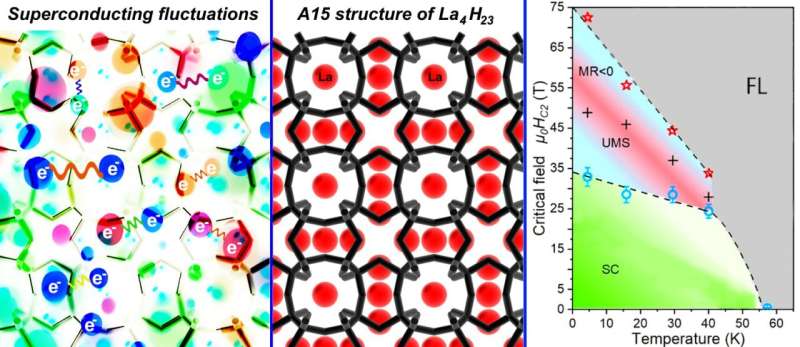
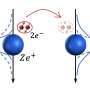
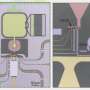
Structure of A15 lanthanum superhydride La4H23 (center), superconducting fluctuations in it (left), and phase diagram of La4H23 in strong magnetic fields (right). Credit: Dmitrii Semenok
Researchers from Skoltech, Jilin University and Beijing HPSTAR in China, and their German colleagues have synthesized and studied a new type of hydrogen-rich superconductor. Technically referred to as an A15-type lanthanum superhydride, with the formula La4H23, it shows superconductivity below minus 168 degrees Celsius at a pressure of 1.2 million atmospheres. The research results were published in the National Science Review.
Polyhydrides are a novel class of compounds synthesized at about 1 million times the normal atmospheric pressure on Earth. They can exhibit unique superconducting properties with record-high critical temperatures of up to -23 C in lanthanum decahydride LaH10, critical magnetic fields reaching 300 tesla, and critical current densities.
Even compared to other similar hydrides, the newly discovered La4H23 behaves unusually: It has a negative temperature coefficient of electrical resistance in a certain pressure range. That is, unlike ordinary metals, with a decrease in temperature its electrical resistance does not decrease but grows, the way it happens in semiconductors and many unconventional superconductors, such as cuprates.
"Initially, hydrides of the structural type A15 were discovered in the europium-hydrogen system, then they were found in the barium-hydrogen and lutetium-hydrogen systems. In the latter, the superconducting hydride La4H23 is formed. We performed first-principles calculations of the thermodynamic stability of these structures and found that the same compound should exist in the lanthanum-hydrogen system. Moreover, it must have an even higher critical temperature of superconductivity," said one of the paper's lead authors, Skoltech Research Engineer Grigoriy Shutov, also a Ph.D. student of computational and data science and engineering, explaining the motivation behind the study.
The synthesized lanthanum hydride La4H23 exhibits other unusual properties. Typically, in magnetic fields, superconducting transitions broaden significantly. The magnetic field creates inhomogeneities in the concentration of Cooper pairs in the volume of the superconductor. As a result, some areas of the sample go to the superconducting state later than others, and the transition seems to "stretch out" on the temperature scale. This is observed for such well-known materials as magnesium diboride, yttrium barium copper oxide, bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide, and others.
In polyhydrides, however, hardly any broadening of superconducting transitions is observed, which is very convenient in experimental practice. This occurs because magnetic vortices, also called Abrikosov vortices, are rigidly attached to existing structural inhomogeneities inside a polyhydride and do not introduce additional disturbances. The situation is different with the new lanthanum superhydride: It exhibits an unexpected narrowing of superconducting transitions.
One of the study's lead authors, Dmitrii Semenok of HPSTAR, who holds a Ph.D. in materials science and engineering from Skoltech, commented, "This unusual behavior made us think about strong pulsed magnetic fields. We took a sample in a diamond anvil cell, prepared by our colleagues from Jilin University, and our curiosity led to another remarkable discovery."
More information: Jianning Guo et al, Unusual metallic state in superconducting A15-type La4H23, National Science Review (2024). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwae149
Provided by Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology