Credit: Opto-Electronic Advances (2024). DOI: 10.29026/oea.2024.240013
Phototherapy is a safe and effective method for tumor treatment, including photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT). PTT refers to the use of laser to activate photothermal conversion agents and use high temperature to kill tumor cells, while PDT stimulates photosensitizers to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill tumor cells.
Studies have shown the combined therapeutic potential of PTT/PDT, but limited by the low oxygen content in tumors, monotherapy is often insufficient to produce efficient and long-term therapeutic effects on tumors.
At the same time, the ability of phototherapy to trigger the immune response against cancer is limited, and local immune stimulation is difficult to activate the systemic anti-tumor immune response. Improving the ability of phototherapy to stimulate the systemic immune response needs further research.
Nitric oxide (NO) has multiple functions in the physiological and pathological processes of the human body, and a critical interaction occurs between it and reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by PDT to form reactive nitrogen species (RNS).
These RNS could enhance the efficacy of PDT under hypoxic conditions by killing tumor cells, while also significantly affecting the immune response.
The current study demonstrates that RNS can suppress immunosuppressive cells and polarize tumor-associated macrophages into M1-like phenotypes. Thus, the strategy of NO/ROS/RNS cascade generation has great potential in activating systemic, long-term anti-tumor immune responses.
However, the generation of RNS is hampered by the difficulty in precisely controlling the location and timing of NO release, as well as the short lifetime (usually 3–6 ms) and limited diffusion range (~ 20 nm) of singlet oxygen.
Using nanoparticles to deliver NO donor and photosensitizer at the same time, and applying laser irradiation to the tumor site to initiate PTT/PDT at the same time, an on-site cascade of NO/ROS/RNS release can be achieved, which can significantly improve the production of RNS and anti-tumor efficacy.
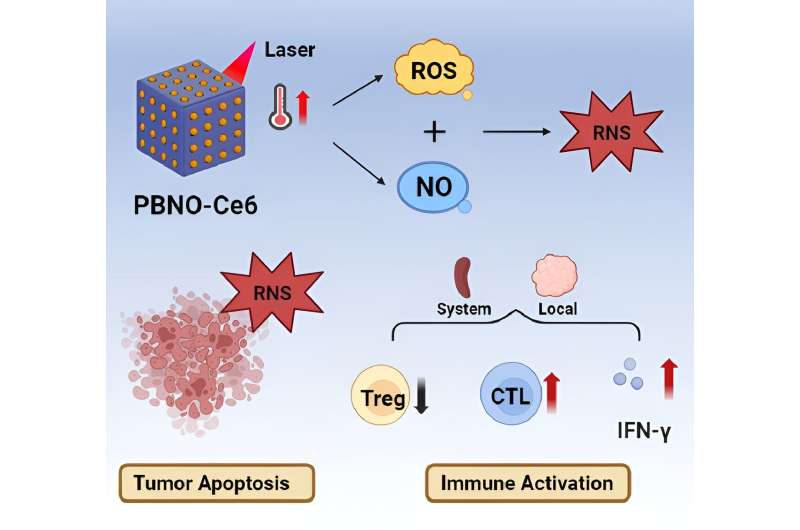
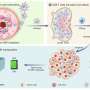
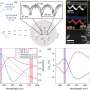
The authors of a new study propose a NIR trigger-activated reactive nitrogen nanoreactor (PBNO-Ce6), which can simultaneously produce nitric oxide (NO), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) on-site to kill tumor cells in vivo, enhance local and systemic long-term anti-tumor immune response, and protect the tissue from the re-attack of tumors. The paper is published in the journal Opto-Electronic Advances.
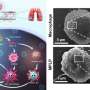
This nanoreactor is based on Prussian blue nanoparticles (PB). PBNO nanoparticles, which can release NO after laser stimulation, were first synthesized by doping sodium nitroprusside (SNP) in the crystal structure of PB as NO donor, and then the photosensitizer Ce6 was loaded on the surface mesopore of the nanoparticles to achieve PTT/PDT combination therapy.
The released NO combines with ROS produced by photosensitizers to RNS, which greatly improves the photodynamic/photothermal therapeutic effect on tumors and activates the anti-tumor immune response.
More information: Ziqing Xu et al, NIR-triggered on-site NO/ROS/RNS nanoreactor: Cascade-amplified photodynamic/photothermal therapy with local and systemic immune responses activation, Opto-Electronic Advances (2024). DOI: 10.29026/oea.2024.240013
Provided by Compuscript Ltd