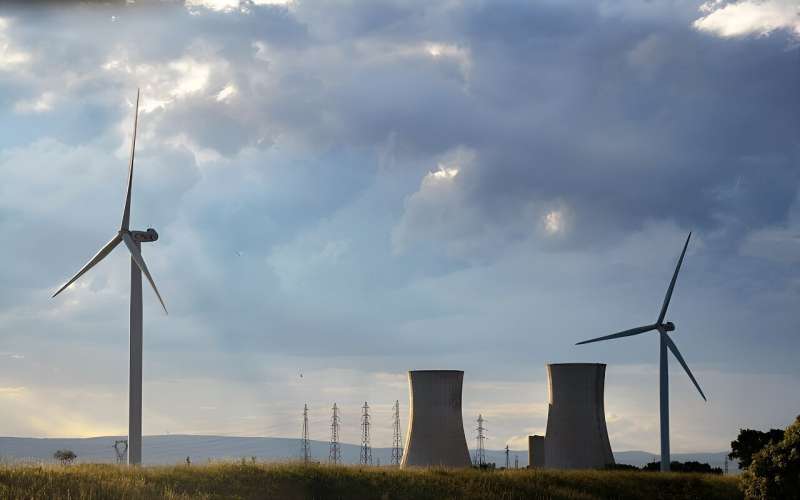
In France’s Drôme region, new wind turbines contrast with the aging Tricastin nuclear power plant, build in the early 1980s. Credit: Jeanne Menjoulet/Wikimedia
Faced with the uncertainties surrounding climate change, policymakers and investors need to know what can happen and how likely these outcomes may be. Unfortunately, current scenarios answer only the first question—and at that, only partially. Research carried out at the EDHEC Risk Climate Institute tries to provide approximate but "actionable" answers to the second.
Climate stress testing dates back to the 1990s, when teams of scientists collaborated to create a scenario framework that was to set the analytical standards for decades to come.
They did so by sketching out a handful of narratives about how the world may evolve, socially and economically. These are now referred to as shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs). The narratives were combined with a range of projected carbon emissions, known as representative carbon pathways (RCPs).
Each narrative was run through every emission projection using process-based integrated assessment models (IAMS), which were fine-tuned on a case-by-case basis to reflect as closely as possible each of the narratives. At this point, the only degree of freedom left to match the narrative with the emission projection was the social cost of carbon—roughly speaking, the tax that should be levied on the "consumers" of carbon emissions, and whose proceeds should be channeled to emission reductions.
The SSP-RCP approach, as it is now known, was endorsed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and has deservedly became a standard framework.
An analysis framework that's showing its age
Despite its strengths, the SSP-RCP approach isn't perfect, nor does it adequately fulfills the need of all scenario users. Indeed, two decades after their introduction, the SSP-RCP approach is showing signs of aging.
We argue that its revision should be carried out along three distinct lines, each addressing one of the problems with the present modeling framework:
- Let's consider the narratives first. They are presented in a rich and colorful language (there is mention of "resurgent nationalism," "growing inequality," etc.), but the only levers at the disposal of the models that try to capture these narratives are the rates of demographic and economic growth, the carbon intensity (emissions per unit of energy) and the energy intensity (energy per unit of GDP). If each of these variables can just exist in three possible states—say, high, medium, and low—that gives us 3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 81 narratives. So, the six narratives chosen by the IPCC are but a small subset of all the possible worlds that may occur.
- Could the IPCC's six narratives be the most likely ones? We cannot tell, because no probabilities were associated to the scenarios—and this, we contend, is the second big shortcoming of current scenarios. Without any probabilistic information, we cannot tell which scenarios we should really worry about, and which can be safely set aside.
- The third problem is the modeling choice in the SSP/RCP set-up, where each narrative is associated with the most likely trajectory for each of the driving variables. This is reasonable, but fails to convey the huge uncertainty around the key estimates. This creates a misplaced sense of predictability, often expressed in tenth-of-degree precision. In reality, knowing how uncertain we are about an outcome can be as important as knowing the expected value for this outcome.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()